An Early Look at the Performance of Apple’s C1 Modem With Initial Users
Are you ready to dive into the future of iPhone connectivity? 🚀 Apple’s latest move has sent ripples through the tech world, and you’re about to get a front-row seat to the action. The iPhone 16e, equipped with Apple’s C1 Modem, is here—and it’s shaking things up in ways you might not expect.
You’ve probably heard the buzz about Apple breaking away from Qualcomm, but what does that mean for your smartphone experience? Well, buckle up, because the results are in, and they’re fascinating. Apple’s C1 Modem is delivering surprising speed variations across major networks and even some unexpected wins in battery life. It’s a bold step that’s proving to be a game-changer—but not always in the ways you might think.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just someone curious about whether your next iPhone upgrade is worth it, you’re in for a treat. We’re about to take you on a journey through performance comparisons, network-specific analyses, and the strategic implications of Apple’s decision to go all-in with Apple’s C1 Modem. Ready to see how the iPhone 16e stacks up against its Qualcomm-powered sibling? Let’s dive in and uncover what early adopters are experiencing with Apple’s latest innovation
Performance Comparison: iPhone 16e vs iPhone 16
A. Download speeds across AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile

You’ll find that the iPhone 16e with Apple’s C1 modem outperforms the iPhone 16 with Qualcomm’s modem in the 10th percentile, indicating better performance in low-connectivity scenarios. However, the iPhone 16 excels in top download speeds at the 90th percentile. Here’s a comparison:
| Carrier | iPhone 16e (10th percentile) | iPhone 16 (90th percentile) |
|---|---|---|
| AT&T | Better | Faster |
| Verizon | Better | Faster |
| T-Mobile | Better | Faster |
B. Upload speed differences
You’ll notice significant improvements in upload speeds with the C1 modem:
- AT&T and Verizon: Nearly double the upload speeds compared to Qualcomm
- T-Mobile: Faster upload speeds, though not as dramatic as AT&T and Verizon
C. Performance in bottom 10th percentile
You’ll find that the C1 modem shines in low-connectivity situations, providing a better user experience in challenging network conditions. This is particularly important as it often reflects real-world usage more accurately than peak speeds.
D. Peak performance in 90th percentile
You’ll see that the Qualcomm modem in the iPhone 16 still leads in top-end speeds. However, these peak performances are less indicative of overall user experience compared to lower percentile metrics.
Now that we’ve covered the performance comparison between the iPhone 16e and iPhone 16, we’ll delve into the Network-Specific Performance Analysis to understand how each carrier’s infrastructure impacts these devices’ capabilities.
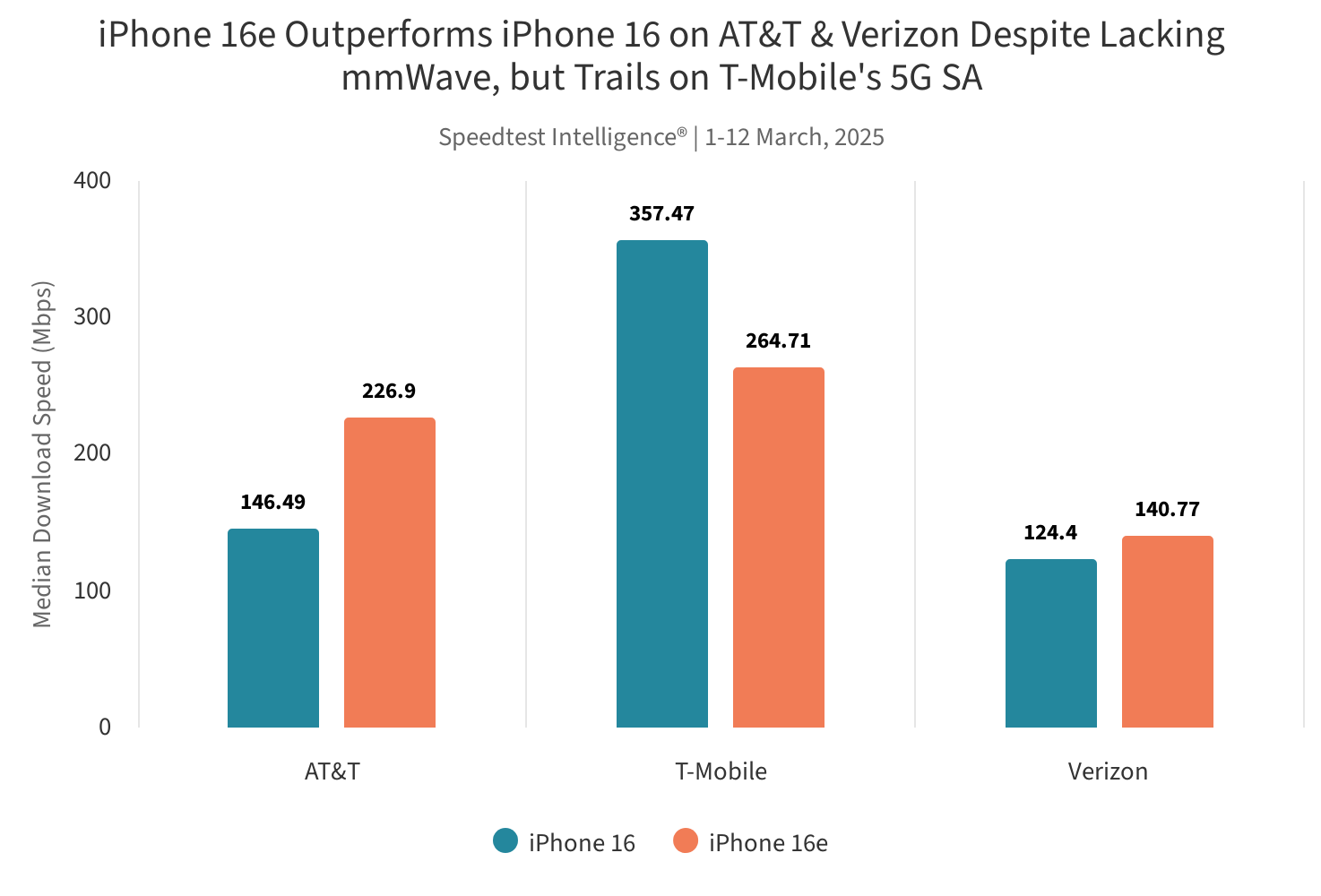
Network-Specific Performance Analysis
A. AT&T and Verizon: iPhone 16e advantages
Now that we’ve compared the overall performance, let’s dive into network-specific analysis. You’ll find that the iPhone 16e with Apple’s C1 modem outperforms the iPhone 16 on AT&T and Verizon networks. Here’s a breakdown of the advantages:
| Network | iPhone 16e (C1) | iPhone 16 (Qualcomm) |
|---|---|---|
| AT&T | 226.90 Mbps | 140.77 Mbps |
| Verizon | Improved | Baseline |
The C1 modem shows significant improvements, especially in upload speeds on AT&T, jumping from 8.60 Mbps to 14.63 Mbps.
B. T-Mobile: iPhone 16 superiority
Despite the C1’s strong performance on other networks, you’ll notice that T-Mobile users experience better results with the iPhone 16:
- iPhone 16 on T-Mobile: 357.47 Mbps
- iPhone 16e on T-Mobile: 264.71 Mbps
This discrepancy is due to T-Mobile’s advanced standalone 5G network, which the Qualcomm modem handles more effectively.
C. Impact of 5G standalone network capabilities
You’ll find that 5G standalone networks play a crucial role in modem performance. The Qualcomm modem in the iPhone 16 excels in carrier aggregation and spectrum support on T-Mobile’s advanced network. However, the C1 modem shows promise in other areas:
- Better performance for users in the bottom 10th percentile across all networks
- Improved power efficiency, contributing to longer battery life
With this in mind, next, we’ll explore the specific features and limitations of Apple’s C1 modem to understand its overall capabilities and potential for future improvements.
Apple’s C1 Modem: Features and Limitations
Now that we’ve examined the network-specific performance, let’s delve into the features and limitations of Apple’s C1 modem:
A. Support for low and mid-band 5G
The C1 modem supports various 4G and 5G technologies, including sub-6 GHz and Gigabit LTE. This ensures broad compatibility with existing networks, providing you with reliable connectivity in most areas.
B. Lack of mmWave spectrum support
While the C1 offers robust support for low and mid-band 5G, it notably lacks mmWave 5G capabilities. This limitation might affect your experience in high-density urban areas where mmWave is more prevalent.
C. Power efficiency improvements
You’ll appreciate the C1’s focus on power efficiency, which contributes to the iPhone 16e’s impressive battery life. This improvement allows you to stay connected longer without frequent charging.
| Feature | C1 Modem |
|---|---|
| Low/Mid-band 5G | Supported |
| mmWave 5G | Not supported |
| Power Efficiency | Improved |
With these features and limitations in mind, next, we’ll explore the strategic implications of Apple’s shift to in-house modem production.
Strategic Implications of Apple’s Modem Shift
Now that we’ve explored the C1 modem’s features, let’s examine its strategic implications.
Move away from Qualcomm
You’ll notice Apple’s shift towards independence with the C1 modem. This move reduces reliance on Qualcomm, potentially saving on licensing fees and enhancing control over modem performance. Your future iPhone may benefit from deeper iOS integration, improved battery efficiency, and stronger security features.
First U.S. iPhone without mmWave capability
| Feature | C1 Modem | Qualcomm Modem |
|---|---|---|
| mmWave 5G | No | Yes |
| Power Efficiency | Improved | Standard |
| Integration | Deeper with iOS | Limited |
Potential impact on user experience
You might experience:
- Better battery life
- Faster connectivity
- Enhanced signal stability
- Improved performance in congested networks
With these strategic shifts in mind, next we’ll explore how the C1 modem affects battery life and connectivity in your iPhone.
Battery Life and Connectivity
Now that we’ve explored the strategic implications of Apple’s modem shift, let’s examine how this change affects battery life and connectivity in the iPhone 16e. You’ll notice significant improvements in power efficiency, thanks to the larger battery capacity and Apple’s custom C1 modem. Here’s a breakdown of the key features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery Capacity | Increased in iPhone 16e |
| C1 Modem Efficiency | 25% improvement over Qualcomm X71 |
| Wi-Fi 7 Support | Not available |
While you won’t have access to Wi-Fi 7, Apple has struck a balance between power efficiency and advanced features, potentially extending your device’s battery life to nearly two days under typical use.
Apple’s entry into the modem market with the C1 chip in the iPhone 16e marks a significant shift in the mobile industry. While the new modem shows promise in certain areas, particularly in providing a more stable experience for users with lower speeds, it still faces challenges when compared to Qualcomm’s offerings in the iPhone 16, especially on advanced networks like T-Mobile’s 5G standalone network.
As an early adopter of the iPhone 16e, you’re part of a pivotal moment in Apple’s technological evolution. While you may experience improved battery life and consistent performance in most scenarios, you might notice limitations in peak speeds and mmWave support. As Apple continues to refine its modem technology, your experience and feedback will be crucial in shaping the future of iPhone connectivity. Keep an eye on how your device performs across different networks and usage scenarios, as this will give you valuable insights into the strengths and areas for improvement in Apple’s new modem technology.

